
Medication Stability Calculator
Calculate medication effectiveness based on temperature exposure duration. Input the temperature and exposure time to determine stability percentage.
Stability Result
When a soldier is deployed to a desert base where temperatures hit 50°C (122°F), their epinephrine auto-injector isn’t just sitting in a backpack-it’s fighting for its effectiveness. The same goes for insulin, vaccines, and antibiotics. In civilian life, a pill left in a hot car for an hour might be a nuisance. In the military, it’s a mission risk. Medications don’t just need to be available-they need to work. And in extreme environments, that’s not guaranteed.
Why Temperature Matters More Than You Think
Most people assume medicine works the same no matter where it’s stored. But that’s not true. Vaccines for anthrax, rabies, yellow fever, and even COVID-19 are designed to stay stable between 2°C and 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Go outside that range, even briefly, and potency drops. U.S. Army data from 2024 shows some vaccines lose up to 50% of their effectiveness in just 30 minutes under direct desert sun. That’s not a small margin-it’s the difference between protection and vulnerability. The problem isn’t just heat. Freezing temperatures can ruin some drugs too. Insulin, for example, can clump and become useless if it freezes. Antibiotics like doxycycline degrade faster above 30°C (86°F). The Army’s Cold Chain Management Principles (April 2025) spell out exact numbers: refrigerated = 2-8°C, frozen = -50°C to -15°C, ultra-cold = -90°C to -60°C. These aren’t suggestions. They’re requirements backed by real-world failures.How the Military Keeps Meds Cold-And Where It Fails
The military uses a system called Cold Chain Management (CCM), which sounds simple: keep meds cold from factory to field. But in practice, it’s a chain of vulnerabilities. Every link matters. A vaccine might start in a refrigerated warehouse, then move to a truck with broken AC, then sit in a tent for hours before reaching a medic. To track this, every storage unit must have two temperature monitors: one digital, one physical. Both must be checked twice a day. If the digital system fails, medics manually log temps every six hours. That’s 45 minutes of extra work per day per unit-time that could be spent treating wounded soldiers. In 2023, Army Medical Logistics Command found that 23% of forward-deployed units had at least one temperature breach. In Camp Arifjan alone, medics recorded 147 incidents in a single year. Even when gear works, the environment doesn’t. Generators fail. Solar panels get dusty. Humidity ruins insulation. One medic on Reddit described modifying MRE coolers with phase-change materials to keep insulin at 4°C for 12 hours in 45°C heat. That’s not standard procedure-it’s improvisation born of necessity.Access Delays Can Be Deadly
It’s not just about keeping meds cold. It’s about getting them to the person who needs them-fast. In temperate zones, a soldier with anaphylaxis gets their epinephrine shot in about 12 minutes. In extreme heat, that jumps to 47 minutes. Why? Because medics are slowed down by protective gear, heat exhaustion, and the need to carry cooled meds in insulated packs while moving under fire or across sand. A 2024 survey of 327 deployed medics found that 68% had seen a medication compromised by heat. Insulin and epinephrine were the most common. One medic lost a vial of insulin after a Humvee’s AC died mid-transit. Another had to wait 90 minutes to get a fever-reducing shot because the only cooler was at a base 12 kilometers away. The military has responded with better gear: insulated backpacks with reusable gel packs that maintain 2-8°C for 6-8 hours in 40°C heat. Success rates? 94%. But these aren’t standard issue everywhere. And they’re heavy. Every extra pound adds to fatigue. Every extra minute spent checking temps is a minute not spent on patient care.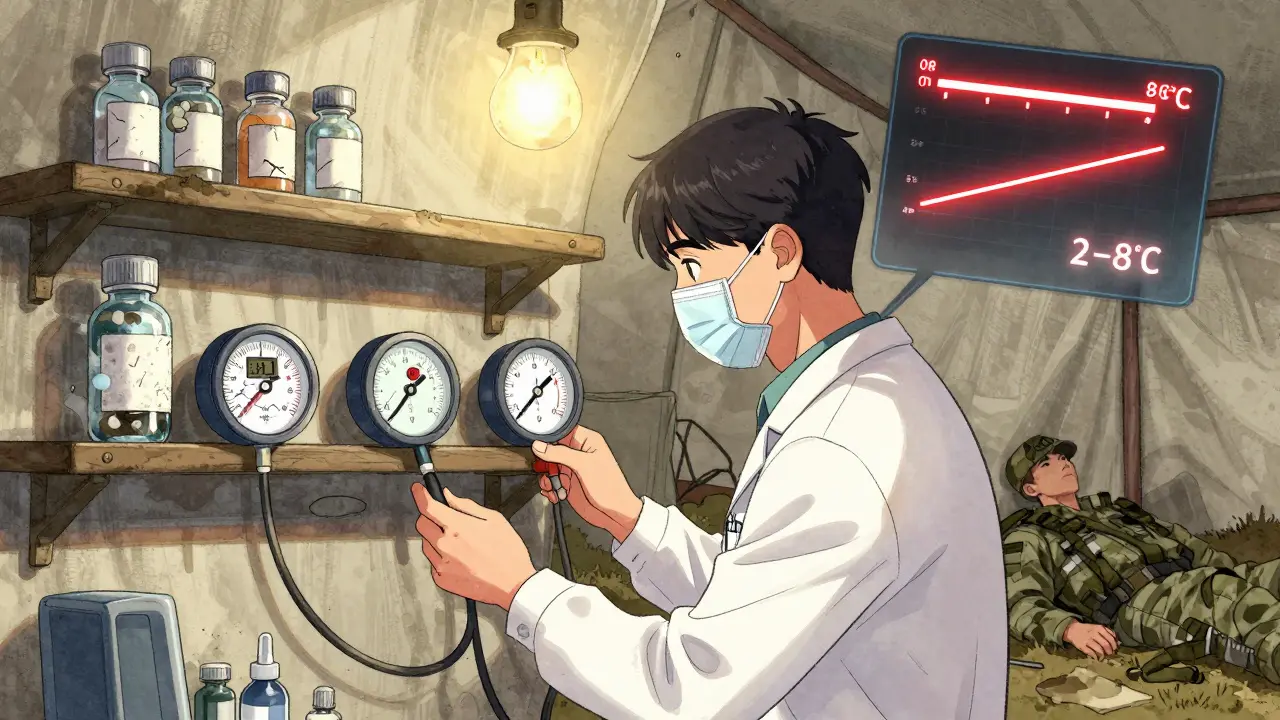
What’s Being Done to Fix It
The military isn’t ignoring the problem. In 2022, they rolled out ‘Temp-Tale’ digital loggers on every shipment. These small devices record temperature throughout transit and flag any breach. Since then, temperature-related medication waste has dropped by $2.3 million annually across CENTCOM theaters. Units report 89% improvement in confidence that their meds are still effective. In 2025, the Army introduced AI-powered predictive modeling at Fort Bragg. The system uses weather data, transport routes, and equipment history to predict where a temperature breach is likely-and redirects shipments before it happens. Early results? A 22% drop in excursions. The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is investing $28 million in something called StablePharm. The goal: develop drugs that stay effective at up to 65°C (149°F). Early tests show heat-sensitive antibiotics are now 40% more stable. That’s huge. Imagine a soldier carrying antibiotics that don’t need refrigeration. No coolers. No logs. No delays.The Bigger Picture: Climate and the Future of Combat Medicine
This isn’t just a logistics issue. It’s a climate issue. Climate Central data shows that Middle Eastern deployment zones had 23 more days above 40°C in 2024 than in 2020. That trend isn’t slowing. The RAND Corporation warns that without next-gen heat-stable drugs, medication efficacy in extreme environments could drop 15-20% by 2030. That means more sick soldiers. More mission failures. More lives at risk. Right now, the military spends $1.2 billion a year on medical logistics. Nearly 38% of that-$456 million-is on temperature-controlled transport. That’s more than the entire annual budget of some small nations’ health systems. And it’s growing.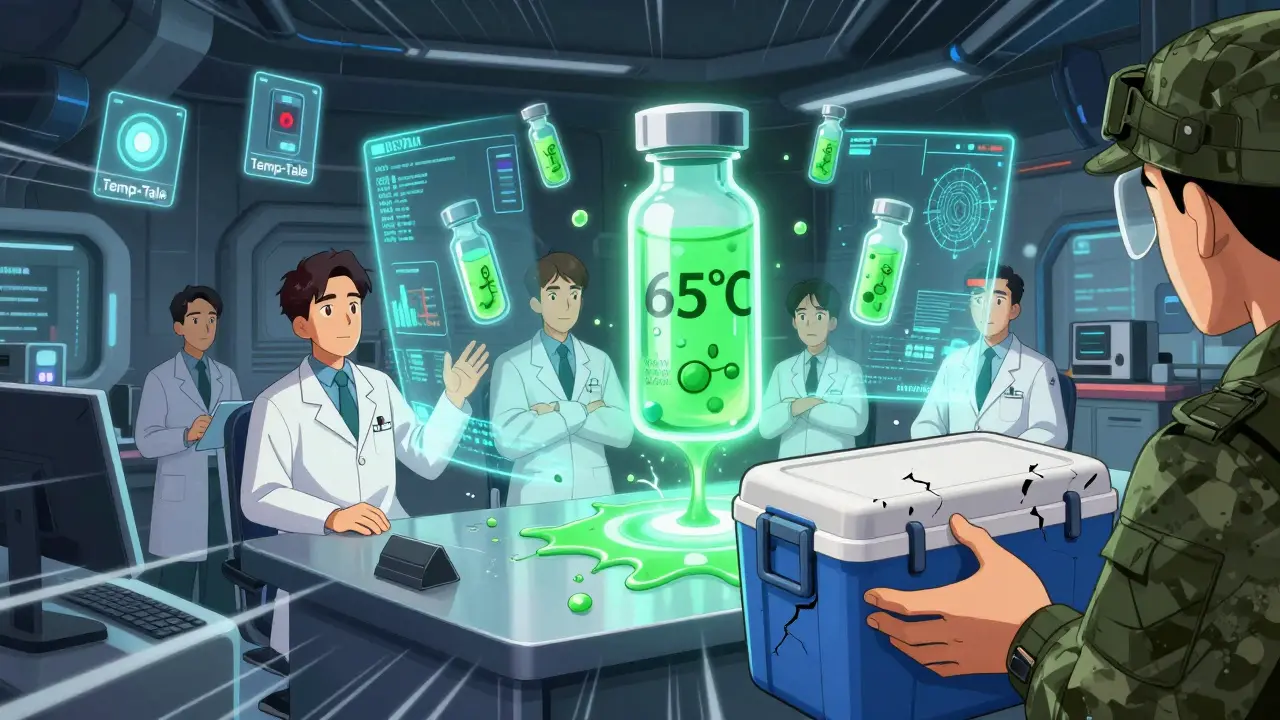
What Soldiers Need to Know
If you’re deployed, you need to treat your meds like weapons. Check the temperature log every morning and afternoon. If a cooler feels warm, don’t assume it’s fine. Report it. Document it. Don’t wait. A single missed log can mean a vaccine doesn’t work-and your whole unit is exposed. If you carry an epinephrine auto-injector, keep it in the inner pocket of your vest, not your backpack. Body heat helps. But don’t leave it in your vehicle. Don’t let it sit in the sun. If you’re in a hot zone, ask your medics about insulated carriers. Know your meds’ limits. Know your unit’s protocols.What’s Next
The future of military medication safety lies in three places: better packaging, smarter tech, and drugs that don’t need refrigeration. By 2028, 75% of military pharmaceuticals are expected to have IoT sensors built into their packaging-real-time tracking, alerts, and data streams. That’s not science fiction. It’s already in testing. But technology alone won’t fix this. Training will. Every medic must complete 40 hours of Cold Chain Management certification, updated quarterly. And it’s working-92% pass. But knowledge only matters if it’s applied. In the field, speed and accuracy matter more than perfect paperwork. The system is getting smarter. But the soldier still has to make it work.What happens if a vaccine is exposed to high heat during deployment?
If a vaccine is exposed to temperatures above 8°C for extended periods, its potency can drop by up to 50% in as little as 30 minutes. This reduces the body’s immune response, leaving soldiers vulnerable to diseases like anthrax, rabies, or yellow fever. Units with documented temperature excursions have shown 12% lower seroconversion rates, meaning fewer soldiers develop protective antibodies.
Are military medication storage rules stricter than civilian ones?
Yes. Civilian pharmacies typically use one temperature monitor and may allow brief excursions without full documentation. The military requires dual verification-both digital and physical logs-and mandates immediate reporting and corrective action for any breach outside 2-8°C. Temperature logs must include root cause analysis, which civilian settings rarely require.
Which medications are most vulnerable to heat in the field?
Insulin and epinephrine auto-injectors are the most vulnerable. Insulin can clump and lose effectiveness if frozen or overheated. Epinephrine’s chemical structure changes under extreme heat, which can alter how quickly it delivers the dose-even if the device still fires. Antibiotics like doxycycline and certain antivirals also degrade rapidly above 30°C (86°F), reducing their ability to fight infection.
How do medics handle medication transport in extreme heat?
Medics use insulated backpacks with phase-change gel packs that maintain 2-8°C for 6-8 hours in 40°C heat. Some modify MRE coolers or use vehicle-mounted refrigerated units. All shipments must include ‘Temp-Tale’ digital loggers to record temperature during transit. In forward areas, medics often carry emergency meds in inner vest pockets to use body heat as a buffer against extreme ambient temperatures.
Is there a plan to make medications that don’t need refrigeration?
Yes. DARPA’s StablePharm program is developing heat-stable versions of antibiotics and vaccines that remain effective up to 65°C (149°F). Early results show 40% improved stability. By 2027, the goal is to field these drugs. If successful, they could eliminate the need for cold chain logistics in most combat zones, reducing weight, complexity, and risk.
How often are temperature logs checked in the field?
In units with digital monitoring, logs are checked twice daily-once in the morning and once in the evening. In units without remote systems, medics must check and record temperatures every six hours. Each check takes about 10 minutes. With 45 minutes of daily logging required per unit, this adds up to significant time away from direct patient care.
Final Thoughts
Medication safety in combat isn’t about fancy labs or high-tech hospitals. It’s about a medic in a dusty tent, checking a thermometer, making sure a vial of insulin hasn’t cooked in the sun. It’s about a soldier carrying a life-saving shot in their vest, knowing it might be their only chance. The military has systems. It has rules. But in the end, it’s the people who make it work. And they’re doing it under conditions no civilian pharmacy ever faces. The stakes? Not just mission success. Survival.14 Comments
Write a comment
More Articles

Buy Cheap Generic Crestor Online - Affordable Cholesterol Medication
Learn how to safely buy cheap generic Crestor online, compare prices, verify legitimate UK pharmacies, and avoid scams while saving on cholesterol medication.
Tick Fever: What You Need to Know About This Dangerous Disease
Tick Fever, also known as Tick-Borne Disease, is a serious illness transmitted by ticks. It's crucial to be aware that this disease can have severe health implications including fever, headache, and fatigue, and in some cases can even be fatal. Early detection and treatment are absolutely vital. It's also important to take steps in preventing tick bites, such as using repellents and wearing appropriate clothing when in tick-infested areas. Stay safe out there, folks!

gary ysturiz
January 12, 2026 AT 14:37Just think about it-soldiers carrying life-saving meds in their vests because the gear failed again. It’s not rocket science. It’s basic human survival. And we’re still making them guess if their epinephrine works?
It’s embarrassing.