Betahistine: What it treats, how to take it, and staying safe
If you're dealing with dizzy spells or Meniere's disease, betahistine is a medicine you'll likely hear about. It’s used mainly to reduce vertigo, tinnitus (ringing in the ear), and the pressure or fullness that comes from inner ear problems. People often notice fewer attacks after a few weeks, but it can take time—so patience matters.
How much to take
Typical adult dosing is 8–16 mg taken two or three times a day, which adds up to about 24–48 mg daily. Doctors may start low and adjust based on how you respond. Take tablets with food if your stomach gets upset. Don’t change dose or stop suddenly without talking to your doctor—sometimes symptoms return if you stop too quickly.
Children and teens should only use betahistine under specialist advice—dosing isn’t standard for younger patients. If you have kidney or liver problems, your doctor will decide the right dose for you.
Side effects and precautions
Most people tolerate betahistine well, but watch for mild side effects like headache, nausea, stomach pain, or skin rash. Serious allergic reactions are rare but need urgent care. Betahistine is not recommended if you have a known pheochromocytoma (a rare adrenal gland tumor) — tell your doctor if you’ve had this condition.
If you’re pregnant, breastfeeding, or planning pregnancy, talk to your doctor. Safety data is limited, so your doctor will weigh benefits against risks. Also tell your provider about all medicines you take—antihistamines and some blood-pressure drugs can affect how betahistine works.
A few practical tips: take your doses at roughly the same times each day, keep a simple diary of attacks so you and your doctor can see if the drug helps, and avoid driving or risky tasks until you know how betahistine affects your balance.
Buying and storing betahistine
In many countries betahistine is a prescription medicine. Don’t buy from random online shops that skip prescriptions—use a licensed pharmacy or a reputable online pharmacy that shows a real contact address and pharmacist support. Ask for product packaging and expiry date when it arrives. If a price looks too low or the seller won’t supply a prescription check, that’s a red flag.
Store tablets at room temperature away from heat and moisture. Keep them out of reach of children. If a pharmacist or doctor gives you extra safety instructions, follow them exactly.
Quick checklist before you start: confirm the diagnosis (vestibular or Meniere’s symptoms), review other meds you take, ask about expected timing for benefit (often weeks), and agree on how you’ll monitor progress. That simple routine helps you and your clinician get better results faster.
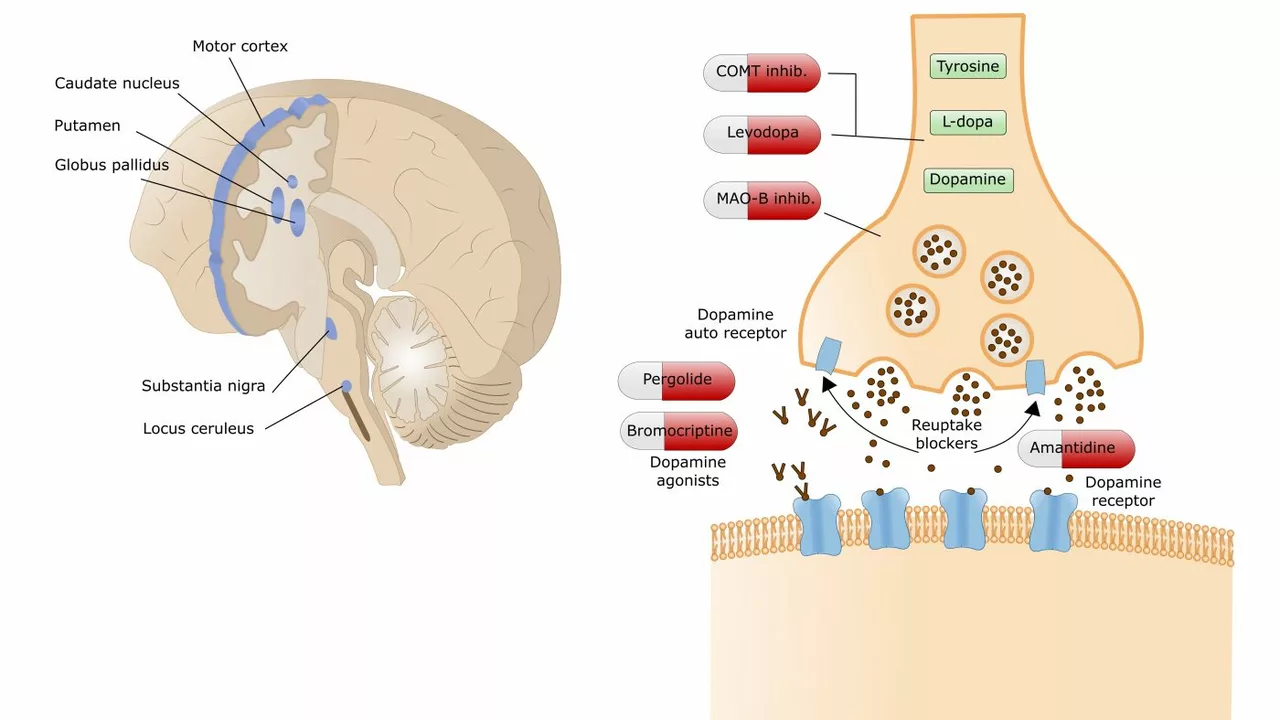
The potential benefits of betahistine for individuals with Parkinson's disease
In my recent exploration, I discovered the potential benefits of Betahistine for those living with Parkinson's disease. This medication, often used for vertigo, could potentially improve symptoms of this neurodegenerative condition. Researchers suggest that Betahistine might have the ability to reduce tremors and improve motor function. There is also a belief that it could enhance cognitive abilities and alleviate depression often associated with Parkinson's disease. However, it's important to note that more research is needed to confirm these potential benefits.